- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding the Basics
- 3. Deep Dive IoT Connectivity Technologies
- 4. Comparative Analysis MNO vs MVNO vs MVNE MVNA
- 5. Business Considerations ROI
- 6. Future Trends in IoT Connectivity
- 7. Real World Use Cases Success Stories
- 8. FAQs and Glossary
- 9. Cellhire A Leading Global MVNO
- 10. Conclusion
- 11. Additional Resources
1. Introduction
The global landscape of IoT connectivity is evolving at a rapid pace. As enterprises seek seamless, international deployments of IoT devices, choosing the right connectivity partner becomes a strategic imperative. This guide delves deep into the differences between Mobile Network Operators (MNOfas) and Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs), while also exploring the supporting roles of MVNEs and MVNAs in today’s connectivity ecosystem.
We have designed this comprehensive resource to provide decision-makers with actionable insights, technical details, pricing and real-world examples, enabling them to choose the most efficient and cost-effective IoT connectivity solution.
2. Understanding the Basics
2.1 What is an MNO?
An MNO (Mobile Network Operator) owns and operates its “own” network infrastructure and holds the necessary spectrum licences. These operators invest in essential infrastructure such as cell towers, base stations, and backhaul networks. They generate revenue by directly providing voice and data services to consumers and businesses, and occasionally, they collaborate with MVNOs to resell network access.
2.2 What is an MVNO?
An MVNO (Mobile Virtual Network Operator) does not own the network infrastructure or spectrum. Instead, it leases network capacity from MNOs to provide voice and data services under its “own” brand. MVNOs often serve niche markets, offering flexible and cost-effective solutions that are especially beneficial in the IoT space. Typically, we categorise them as either "thin" MVNOs, which outsource most functions, or "thick"/full MVNOs, which manage more in-house operations.
2.3 Key Terms and Glossary
Below is a brief glossary of key terms:
- MNO: Mobile Network Operator – owns and manages network infrastructure and spectrum licences.
- MVNO: Mobile Virtual Network Operator – leases network access from MNOs to offer connectivity services.
- MVNE: Mobile Virtual Network Enabler – provides technical infrastructure and support for MVNO operations.
- MVNA: Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator – acts as a broker, facilitating network access for multiple MVNOs.
- eSIM: Embedded SIM technology that enables dynamic switching between networks.
- NB-IoT, LTE-M, 5G IoT, LPWAN: Various cellular and low-power technologies that enable IoT connectivity.
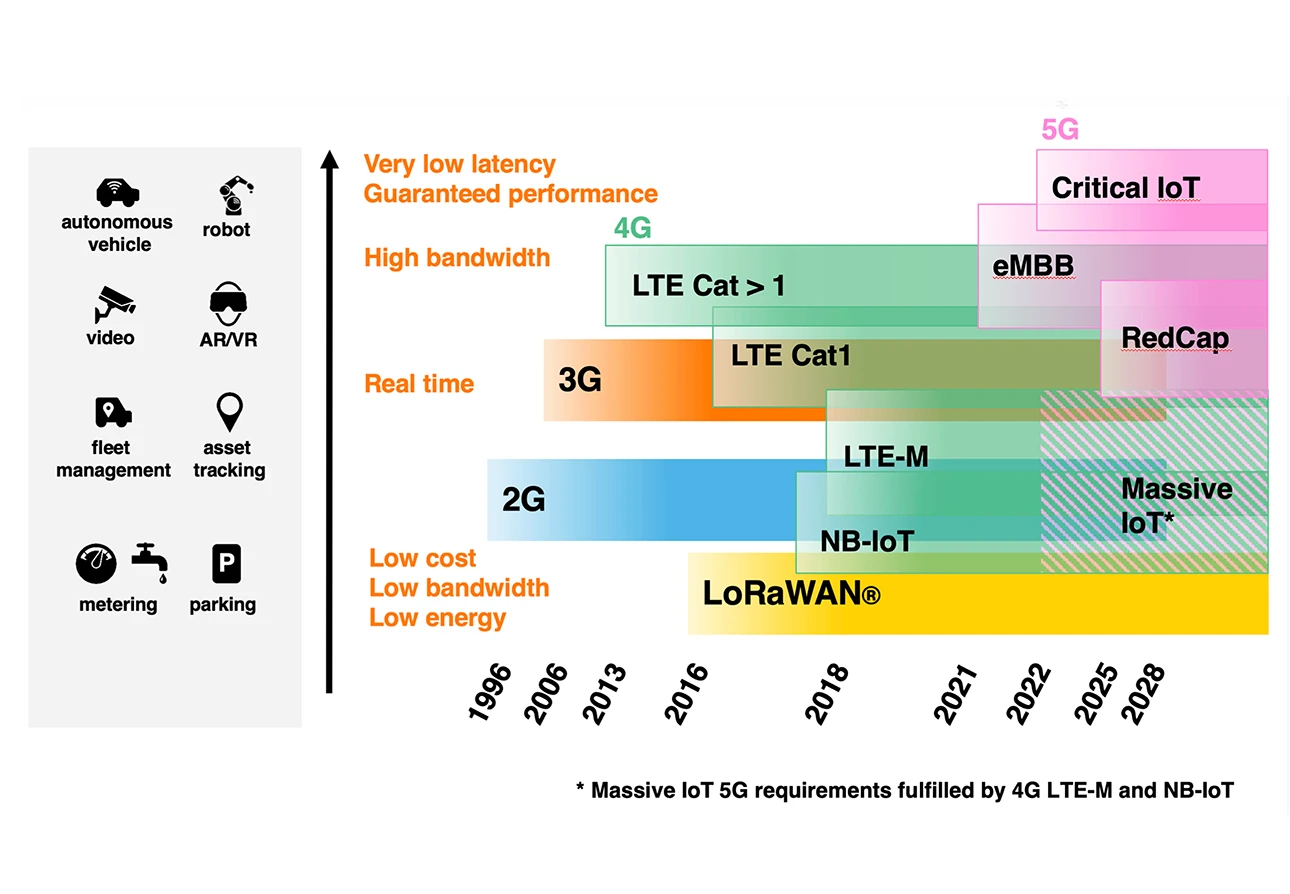
3. Deep Dive: IoT Connectivity Technologies
3.1 Cellular IoT Technologies Explained
Modern IoT connectivity relies on a range of cellular technologies. Understanding these options is crucial for selecting the right solution:
- LTE-M balances extended coverage with higher data speeds and better mobility support compared to NB-IoT.
- 5G IoT: Offers ultra-low latency and high throughput, enabling mission-critical applications.
- Non-cellular LPWANs (LoRa, Sigfox): Provide long-range connectivity at low power, suitable for remote monitoring and asset tracking.
- NB-IoT is optimised for low data rates and extended coverage, making it ideal for battery-operated sensors.
IoT Connectivity Technologies Comparison
| Technology | Range | Data Rate | Power Efficiency | Mobility Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB‑IoT | High | Very Low | Excellent | No |
| LTE‑M | Medium–High | Low–Medium (~1 Mbps) | Very Good | Yes |
| 5G IoT | Regional–Global | High–Very High | Moderate–Low | Yes |
| LPWAN | Long | Ultra-Low (Sigfox/LoRa) | Excellent | No |
How They Fit Together
Deployment Context: LPWAN for long-range/low-data scenarios; NB‑IoT for static, licensed spectrum; LTE‑M for roaming and mobility; 5G serves real-time, high-data use cases.
Hybrid Strategies: Many IoT projects combine multiple technologies. For instance, NB‑IoT is used for basic sensors, LTE‑M for mobile nodes, and 5G for edge analytics hubs.
3.2 Evolution of eSIM Technology
eSIM technology has fundamentally transformed IoT connectivity by allowing devices to switch between networks dynamically. This capability is especially important for global IoT deployments to ensure continuous connectivity regardless of the device's geographic location.
4. Comparative Analysis: MNO vs. MVNO vs. MVNE/MVNA
4.1 Side-by-Side Comparison
Below is a comparison of MNOs, MVNOs, and the supporting roles of MVNEs/MVNAs based on several key criteria:
-
Infrastructure Ownership:
- MNO: Owns and operates the network.
- MVNO: Leases capacity from MNOs.
- MVNE/MVNA: Provides infrastructure support or brokers access.
-
Control Over Pricing:
- MNO: Typically offers high control over pricing.
- MVNO: Offers variable pricing, often catering to niche markets.
- MVNE/MVNA: Not directly involved in pricing; instead, they enable MVNO operations.
-
Global Reach:
- MNO: Usually confined to regional operations or limited roaming.
- MVNO: Optimised for international coverage by partnering with multiple MNOs.
- MVNE/MVNA: Aggregates access to enhance global connectivity.
-
Flexibility & Scalability:
- MNO: Limited to the network infrastructure they own.
- MVNO: Highly flexible by leveraging multiple carrier partnerships.
- MVNE/MVNA: Provides scalable support for MVNOs.
4.2 Detailed Pros and Cons
MNO Pros
- Extensive network infrastructure.
- MNOs enjoy greater control over network management.
MNO Cons
- The MNO has limited international coverage and roaming options.
- Expanding globally could potentially result in higher costs.
MVNO Pros
- Cost-effective and flexible connectivity solutions.
- MVNOs can provide global coverage by leveraging partnerships and eSIM technology.
MVNO Cons
- Dependence on third-party networks can sometimes result in variable service quality.
5. Business Considerations & ROI
5.1 Pricing Models and Cost Analysis
Effective IoT rollouts require not only connectivity but also a cost model that scales predictably and supports growth. Here's a refined view of pricing strategies, real-world examples, and ROI levers:
Understanding the pricing models is crucial for budgeting and calculating ROI.
Key considerations include
- Setup fees and recurring charges are crucial considerations.
- There are volume discounts and bundled data packages available.
- Evaluate the costs and benefits of working with various MNOs compared to using a single MVNO solution.
IoT Connectivity Pricing Models
Research by IoT Analytics, a leading global provider of market insights and strategic business intelligence for the IoT, AI, Cloud, Edge, and Industry 4.0, identifies three fundamental pricing structures typically offered by MNOs and MVNOs:
- Time-based: Fixed monthly fee for a capped data allowance (e.g., 100 MB). This method is beneficial when one's usage patterns are predictable.
- Usage-based: Costs vary per MB or GB consumed, offering flexibility but less predictability.
- Hybrid: Combines a base plan with a data allotment and adds overage charges for excess usage.
Additionally, providers may charge:
- SIM provisioning fees, device activation costs, and contract minimums
- Billing cycle terms, data speed tiers, and optional service bundles (e.g., static IP, security)
Cost Benchmarks: MVNO vs. MNO
MVNOs like Cellhire generally offer significant cost savings due to lower overhead and IoT-focused pricing plans.
Here's a comparison:
- United Kingdom IoT Pricing: In the UK market, MVNOs undercut MNOs:
- MVNOs like Cellhire offer 10 MB at £1/month (around £2 – significantly below MNO packages).
- Standard packages from UK MNOs (EE, Vodafone, O2, and Three) typically begin around £3–£6 for 10 MB, with higher tiers for larger data volumes.
Cellhire Savings Calculator: Use the Cellhire calculator
To quantify your potential savings, try Cellhire's IoT Data Savings Calculator. It compares your current MNO-based cost, data usage, and SIM count against Cellhire’s MVNO pricing model to estimate annual savings.
- Example Saving Scenario: If you're using 1,000 SIMs, each consuming 50 MB/month, MNO pricing might reach £6,000/month, whereas MVNO plans through Cellhire could drop this to around £2,000/month, saving you about £4,000/month in savings.
Why MVNOs Win on Price
- Lower operational overheads: No need for spectrum licensing or national infrastructure.
- Optimised pricing models: IoT-based, usage-sensitive packages tailored to low-data applications.
- Economies of scale occur when MVNOs aggregate demand from hundreds of thousands of SIMs, which unlocks bulk pricing.
For enterprises managing large IoT estates, especially in the UK, switching from MNO to MVNO, particularly a Full MVNO like Cellhire, can yield 30–60% cost savings. Use the Cellhire calculator to model your specific usage and uncover your potential savings before negotiation.
Remember that you can unlock resilient, multi-network IoT connectivity not just in the UK but across 191 countries. You will have access to EE, O2, Vodafone, and Three, as well as over 430 global networks.
5.2 Checklist: Operational challenges and best practices
Deploying IoT at scale isn't just about price; it’s also about security, compliance, and the ability to grow.
- Security: Implement robust encryption, secure SIM provisioning, and adhere to regional compliance standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigate data sovereignty issues and manage roaming restrictions effectively.
- Scalability: Choose solutions that can grow with evolving business needs.
This checklist of best practices can help you and your business in mitigating risks and ensuring a smooth deployment process.
-
Security:
- Encrypt data in transit (TLS/SSL) and at rest
- Use Identity & Access Management (IAM) with multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls
- Use secure SIM provisioning methods (OTA, SGP)
- Monitor with intrusion detection/prevention systems and firewalls
- Secure OTA firmware updates and update servers
- Detect compromised or rogue devices early
- Restrict backend access only to approved networks
- Conduct regular audits, vulnerability scans, and incident-response drills
- Use AI/ML-driven tools for proactive anomaly detection
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- Map data flows and complete privacy impact analyses
- Adhere to regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA)
- Implement data minimization, anonymization, and consent mechanisms
- Deploy certified hardware/software (e.g., PTCRB, CE, FCC, ETSI, ISO standards)
- Obtain market-specific approvals (ETSI, FCC, etc.)
- Use third-party audits and security certifications (e.g., ISO 27000, IEC 62443)
-
Scalability:
- Plan network capacity and elasticity from the outset
- Use lightweight IoT protocols (e.g., MQTT, CoAP) with staggered data transfers
- Automate SIM/device provisioning via APIs and CMPs
- Enable OTA SIM- and firmware updates for remote management
- Offer network flexibility (private APN, VPN, hybrid MVNO/MNO)
- Maintain compatibility across devices and integration platforms
- Track performance metrics and iterate system improvements
- Use edge computing to reduce latency and offload central systems
6. Future Trends in IoT Connectivity
6.1 Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are shaping the future of IoT connectivity.
- 5G IoT: Ofers ultra-low latency and high-speed data transfer.
- AI-Driven Network Management: Offers predictive maintenance and optimised routing.
- Next-Generation eSIMs: Enhances flexibility and global reach through dynamic network switching.
These technologies are poised to revolutionise how devices connect and communicate on a global scale.
6.2 Expert Opinions & Industry Predictions
Industry experts predict significant changes in the IoT connectivity landscape over the next 5–10 years. The integration of AI, 5G, and advanced eSIM technology will drive innovation, leading to more robust and efficient global connectivity solutions.
7. Real-World Use Cases & Success Stories
Real-world examples provide tangible evidence of how the right connectivity model can transform IoT deployments:
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring systems benefit from reliable MVNO connectivity.
- Automotive: Connected vehicles and fleet management leverage global roaming for enhanced safety and efficiency.
- Smart Cities: Urban infrastructure and utility networks employ scalable, operator-agnostic solutions to ensure seamless connectivity.
For more detailed case studies across diverse industries, refer to our applications page.
8. FAQs and Glossary
8.1 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary difference between an MNO and an MVNO?
MNOs own and operate their network infrastructure, while MVNOs lease network access from MNOs, offering flexible connectivity solutions.
2. How do IoT MVNOs achieve global connectivity?
By partnering with multiple MNOs worldwide and leveraging advanced eSIM technology, MVNOs ensure devices remain connected regardless of location.
3. What are the benefits of using an MVNO for IoT deployments?
MVNOs provide cost-effective, scalable connectivity and simplify management through flexible, operator-agnostic solutions.
4. Are there any security concerns with IoT MVNOs?
While MVNOs offer flexibility, it is essential to evaluate their security protocols, data encryption practices, and adherence to regional regulations to ensure data protection.
5. What future trends should enterprises watch in IoT connectivity?
Key trends include advancements in 5G IoT, AI-driven network management, and next-generation eSIM technology that promises enhanced flexibility and performance.
9. Cellhire: A Leading Global MVNO
Cellhire stands out as a leader in the global MVNO space through its innovative approach and robust infrastructure. Unlike many MVNOs that solely rely on leased network capacity, Cellhire owns and operates its core mobile network, ensuring a solid foundation for global connectivity. This full MVNO model supports a future-ready, forward-looking product range that is engineered for the demands of modern connectivity, including cutting-edge IoT solutions.
Cellhire's MVNO Offering:
-
eSIMsmart: Cellhire launched its eSIMsmart MVNO in 2021. Cellhire’s eSIMsmart leverages advanced eSIM technology to deliver seamless global connectivity. This platform is designed to meet the dynamic needs of enterprises and IoT devices, enabling them to switch networks effortlessly and remain connected worldwide.
-
Wholesale Provider Role: In addition to serving its own customers, Cellhire acts as a wholesale provider, offering white-label MVNO services and connectivity solutions to other businesses and wholesale IoT partners. This role underscores its commitment to fostering a flexible, interconnected global connectivity ecosystem.
-
IoT Connectivity Solutions: Beyond traditional mobile services, Cellhire is recognised for its robust IoT connectivity offerings. By leveraging its IoT network and partnerships with multiple global MNOs, Cellhire ensures that enterprises can confidently and reliably deploy IoT solutions. Cellhire ensures that enterprises can confidently and reliably deploy IoT solutions.
-
Strategic Partnership with Orange:
- Since 1997, Cellhire has partnered closely with Orange Wholesale France, supporting its MVNO strategy.
- In October 2023, this collaboration was elevated with a game-changing framework agreement aimed at expanding MVNO services and rolling out a “light MVNO” product for voice and data in France.
- As a result, Cellhire now offers enhanced IoT roaming coverage spanning more than 191 countries and 430+ network operators.
-
Global Network Partnerships:
- Cellhire maintains direct partnerships and white-label programme with numerous MNOs, including O2, Telefónica UK, EE/BT, Orange France, Verizon, and more.
- These alliances, combined with its own infrastructure, ensure dependable and competitive connectivity solutions across EMEA, the Americas, and APAC.
Through this investment in infrastructure, strategic partnerships, and continual innovation, Cellhire exemplifies a future-ready MVNO. Our capabilities make us a game-changing partner for organisations, optimising their global IoT and connectivity strategies.
10. Conclusion
In today’s global market, selecting the right connectivity model is crucial for the success of IoT deployments. By understanding the distinct roles and benefits of MNOs, MVNOs, and their supporting partners (MVNEs/MVNAs), enterprises can make informed decisions that balance cost, scalability, and performance.
With ongoing advancements in 5G, AI, and eSIM technologies, the future of IoT connectivity looks set to offer even more robust and flexible solutions.
11. Additional Resources
For further insights, "Download our Cellular IoT Connectivity Whitepaper" – a resource for partners operating within the channel. It explains how IoT connectivity serves as the gateway to unlocking new customer bases and revenue streams for your business.
What's included:
- Understanding cellular IoT connectivity
- Choosing a cellular connectivity type
- Why Channel Partners should offer IoT connectivity
- What the future holds for IoT connectivity
Get in touch with a member of our team today or take advantage of our IoT SIM Card Free Trial Pack
